Increasing interest in seafloor mining of massive sulfide deposits over the long term is driven by expected a rising prices of metals b increasing demand for metals or c both rising prices and increasing demand.
Increasing interest in ocean floor mining of massive sulfide deposits.
The term has been coined by mineral explorers to differentiate the modern deposit from the ancient.
Compliance with ethics guidelines.
As hydrothermal systems age the mineral deposits eventually become severed from the heat source and fluid flow pathways responsible for their formation and become.
Current development activity is focusing on ocean floor mining.
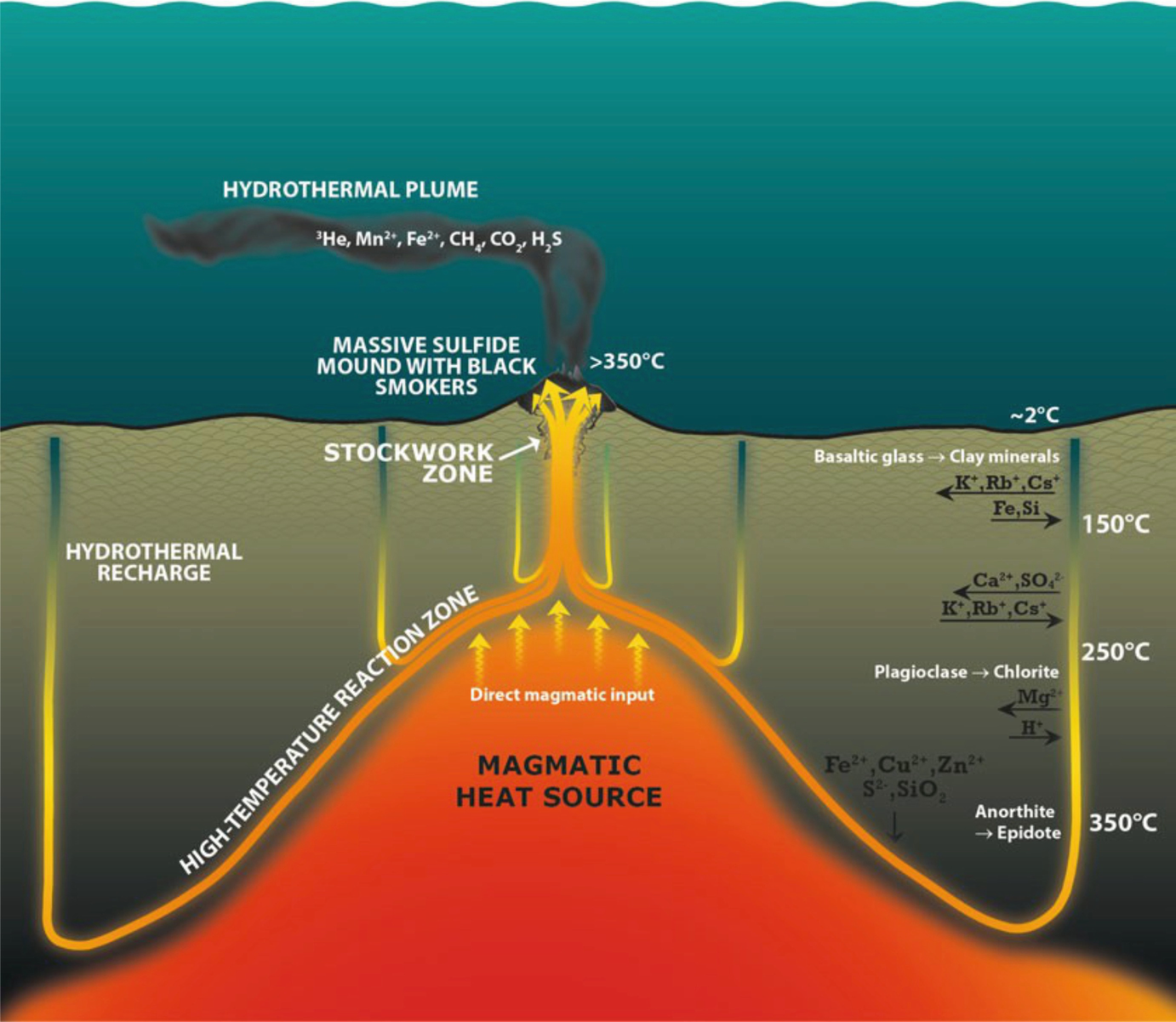
Seafloor massive sulfide deposits or sms deposits are modern equivalents of ancient volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposits or vms deposits.
Sms deposits were first recognized during the exploration of the deep oceans and the mid ocean ridge spreading centers in the early 1960s.
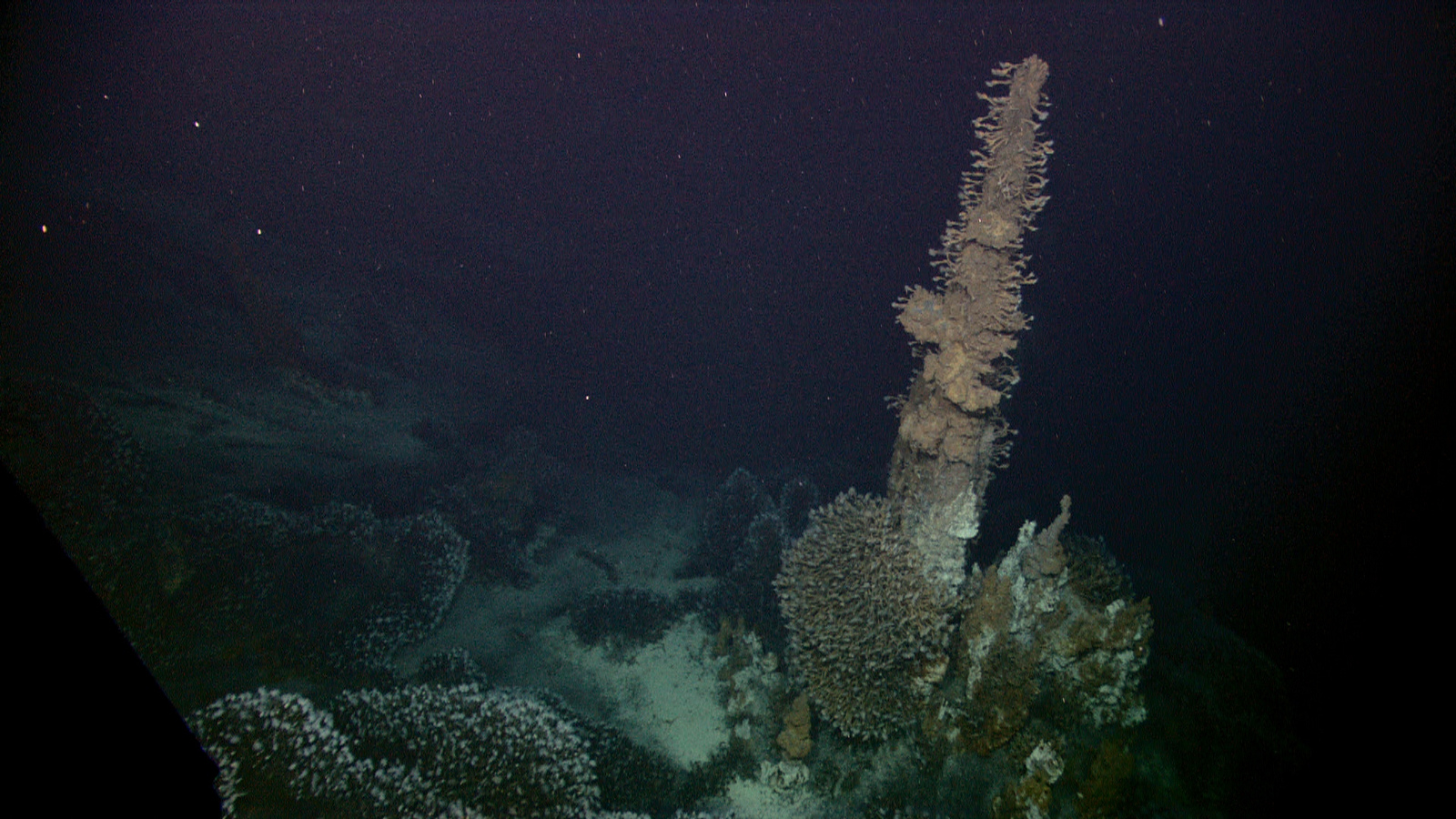
Hydrothermal activity results in the formation of hydrothermal mineral deposits including seafloor massive sulfide deposits at oceanic spreading ridges arcs and back arcs.
The vents create globular or massive sulfide deposits which contain valuable metals such as silver gold copper.
Rising prices of metals b.
4 novel mining technologies are being developed to identify and exploit previously unattainable resources in order to meet the rising global demand.
The island of cyprus for example holds 30 massive sulfide deposits which were a main source of copper for ancient rome.
The solwara 1 seafloor massive sulfide deposit off papua new guinea is relatively small with an inferred total mineral resource of 1 4 million tonnes at a grade of 8 cu and 6 g t au.
Most would probably not be of much interest to the mining industry.
Many deposits are of a tonnage and mineral grade comparable to land deposits and are attractive to mining companies.
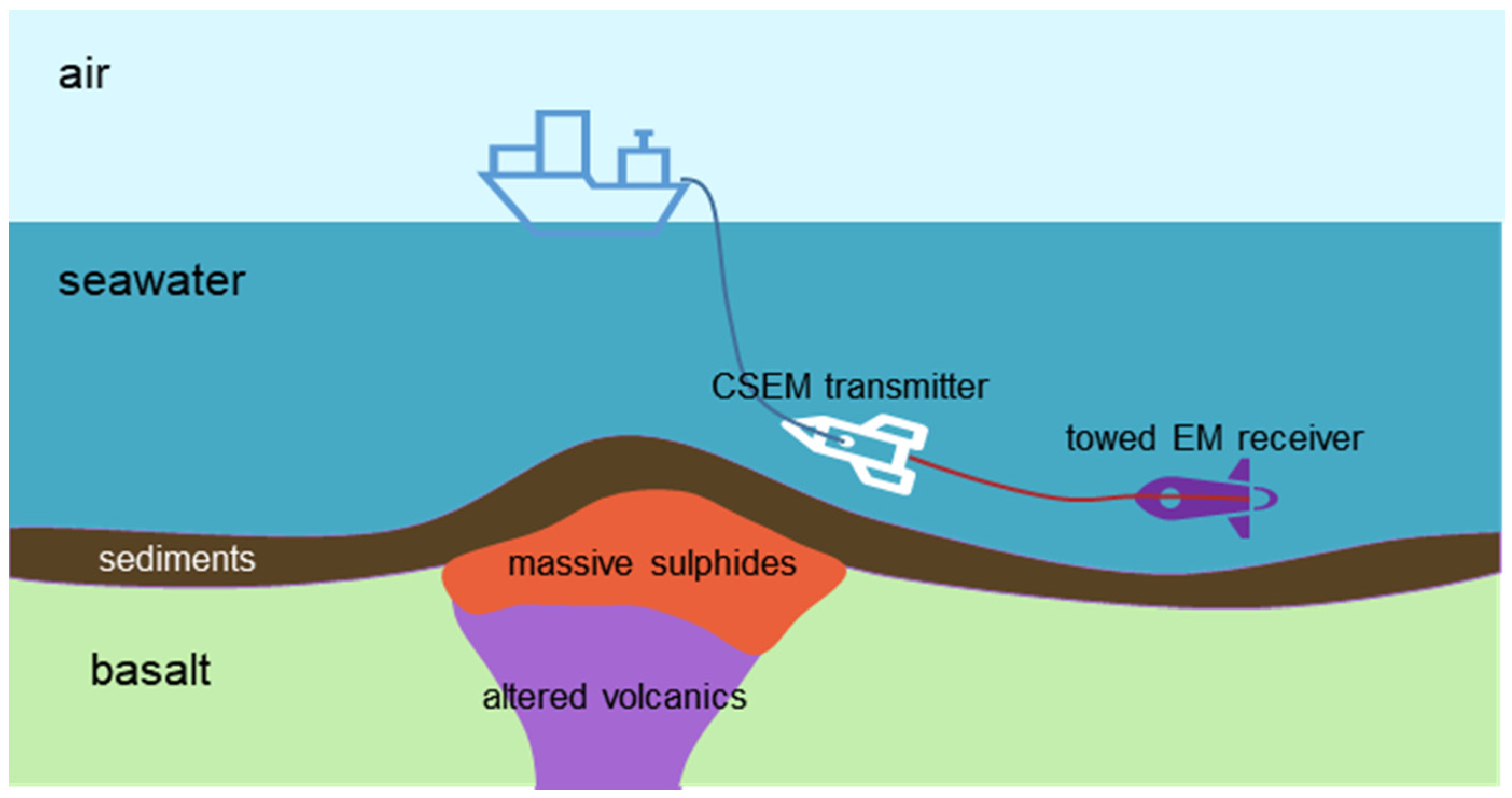
Seabed mining that specifically targets seafloor massive sulfide deposits iron manganese crusts and metallic nodules requires new approaches to material recovery.
By comparison ancient volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits on land can contain resources of 150 million tonnes.
Economically viable deposits can be either active or inactive with different biological communities present at each.
Both rising prices and increasing demand.
The island of cyprus for example holds 30 massive sulfide deposits which were a main source of copper for ancient rome.
So far about 200 active vent fields have been found.
The vast majority of deposits are really small said german.
Increasing interest in ocean floor mining of massive sulfide deposits over the long term is driven by expected.
Deep sea mining is a mineral retrieval process that takes place on the ocean floor ocean mining sites are usually around large areas of polymetallic nodules or active and extinct hydrothermal vents at 1 400 to 3 700 metres 4 600 to 12 100 ft below the ocean s surface.